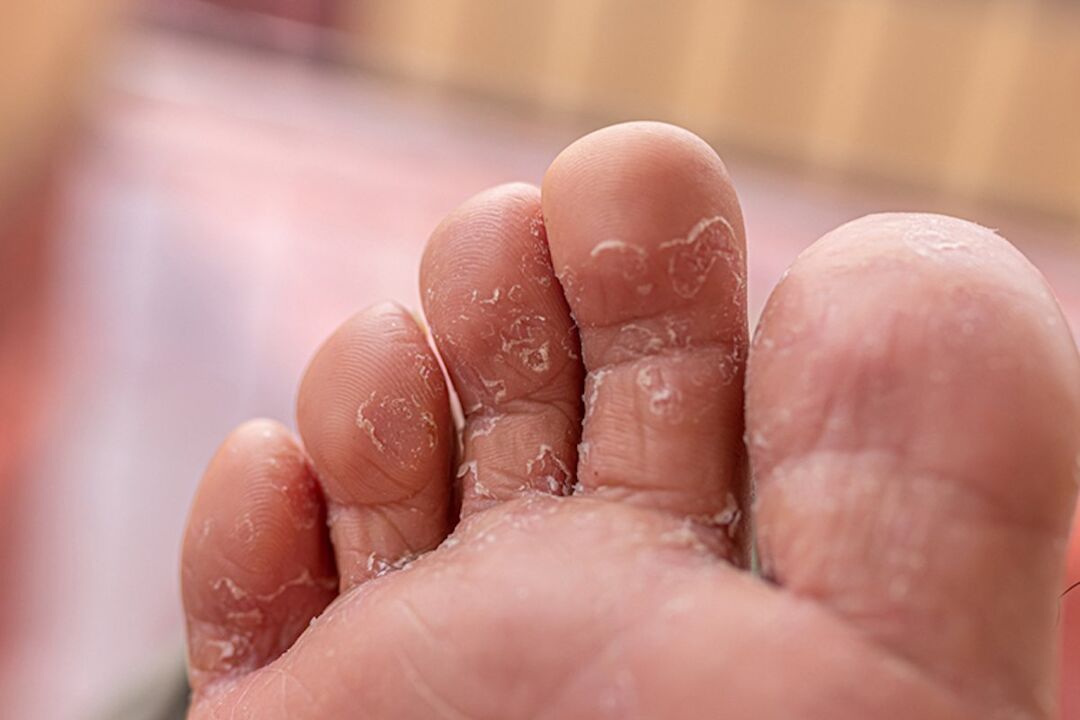
Interdigital mycosis is a fungal infection of the skin in the spaces between the fingers, the causative agent of which is opportunistic organisms and anthropophilic fungi.
Causes of yeast infections
The cause of any yeast infection is contact with an infected person, wearing their shoes or sharing personal hygiene items with them. The risk of infection increases in those with reduced immunity - due to chronic diseases, taking certain medications or vitamin deficiency.
Patients at risk are:
- disorders in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- diabetes mellitus and its complications (especially diabetic foot);
- allergic dermatitis;
- varicose veins;
- obesity;
- increased sweating;
- immune disorders;
- hormonal disorders;
- metabolic disorders in the body, etc.
The skin of the feet after a careful pedicure is extremely vulnerable to fungus. And wearing shoes that are too tight can make the situation significantly worse.
Symptoms
Interdigital mycosis manifests itself in the early stages by slight itching of the skin between the toes. Later, peeling of the skin, redness and the appearance of cracks are added to this symptom.
If you do not take action and consult a specialist, the problem gradually worsens - burning, diaper rash and swelling of the area between the fingers appear. Small bubbles prone to coalescence may begin to form in the interdigital folds. When these bubbles burst, oozing erosions remain in their place and become covered with crusts. This condition is dangerous due to infection - the wounds can fester.
It is important to note that with a long course of interdigital mycosis, the forms of the disease can transform into each other or develop in parallel.
Interdigital mycosis can also occur in an erased form - in this case, the patient periodically experiences unpleasant symptoms of the disease (usually during and after water procedures and with excessive sweating of the feet).
Diagnosis of fungus between the toes
As practice shows, in approximately every third case of skin lesions between the toes, a fungal infection is diagnosed.
When prescribing treatment for mycoses, the podiatrist takes into account many factors: the presence or absence of concomitant pathologies in the patient, the clinical picture of the disease, its form and degree.
Diagnosis of a specific pathogen is the key to effective treatment and successful recovery. To determine which fungus needs to be combated, the podiatrist may order laboratory tests and a bacterial culture for the patient.
How to treat interdigital fungus?
For interdigital mycoses, complex therapy is carried out. He understands:
- topical antifungal medications (creams, lotions, ointments, etc. );
- It is also possible to take oral antifungals.
The course of treatment is determined individually for the patient. Traditional medicine (compresses, baths, lotions based on medicinal plants, etc. ) can be used as auxiliary methods, but only after consultation with a specialist.
If mycosis develops against the background of internal diseases, local therapy is combined with the treatment of the underlying pathology.
Contraindications and possible complications
Interdigital mycosis requires referral to a specialist and complex therapy. Without prompt treatment, it quickly spreads to the entire foot and affects the nails.
In addition, in patients with mycosis, the body's susceptibility to viral diseases increases and the risk of bacterial infection and allergic reactions increases.
Strict adherence to the podiatrist's recommendations and comprehensive treatment are important. Pathogens can become resistant to the drugs used, and combined with repeated infections, it is much more difficult to get rid of the infection - even if there is positive dynamics, treatment cannot be interrupted.
Advice and recommendations from a podiatrist
To avoid fungal infections, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the rules of personal hygiene - this applies, first of all, to personal hygiene items and shoes.
- Do not wear someone else's shoes and only use individual bath towels.
- Do not walk barefoot in a bathhouse, sauna or swimming pool - this is an ideal environment for the growth of fungus, because it is always hot and very humid.
- If you experience excessive sweating of the skin on your feet, you should consult a podiatrist about the use of anti-hyperhidrosis medications.
- Avoid wearing shoes that are too tight and avoid synthetic socks and stockings, which do not allow the skin to "breathe".
To care for the skin of the feet, podiatrists recommend giving preference to hardware methods - the trimmed pedicure is today considered outdated and dangerous. It is very difficult to control how pedicure tools are cut - the risk of infection increases significantly. With a hardware pedicure, the risk of infection is excluded.